Explain @Autowired annotation with example?
Explain @Autowired annotation with example?Ans : The `@Autowired` annotation in Spring is used for automatic dependency injection. It allows Spring to resolve and inject collaborating beans into our bean. This annotation can be applied to constructors, methods, and fields to indicate that Spring should automatically wire the required dependencies.
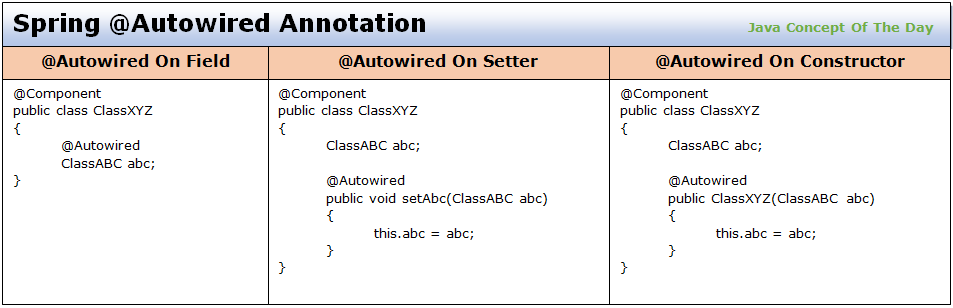
Table of Contents
Example
Step 1: Create a Spring Boot Application
Ensure you have the necessary dependencies in your `pom.xml` (for Maven) or `build.gradle` (for Gradle).
Maven Dependency:
```xml
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
</dependency>
```
Gradle Dependency:
```groovy
implementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter'
```
Step 2: Create the Main Application Class
Create the main class for the Spring Boot application.
```java
package com.example.demo;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class DemoApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(DemoApplication.class, args);
}
}
```
Explanation:
@SpringBootApplication: Indicates a configuration class that declares one or more@Beanmethods and also triggers auto-configuration and component scanning.
Step 3: Create a Service
Create a simple service class that will be injected into another component.
```java
package com.example.demo.service;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
public class GreetingService {
public String getGreeting() {
return "Hello, World!";
}
}
```
Explanation:
@Service: Indicates that this class is a service holding the business logic.
Step 4: Create a Controller
Create a controller class that uses the GreetingService, and apply the @Autowired annotation.
```java
package com.example.demo.controller;
import com.example.demo.service.GreetingService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/web")
public class HelloController {
private final GreetingService greetingService;
@Autowired
public HelloController(GreetingService greetingService) {
this.greetingService = greetingService;
}
@GetMapping("/hello")
public String sayHello() {
return greetingService.getGreeting();
}
}
```
Explanation:
@Autowired: Injects theGreetingServiceinto theHelloControllervia constructor injection.sayHello: Method that uses theGreetingServiceto get a greeting message.
Step 5: Running the Application
Run the application from the main class (`DemoApplication`). When you navigate to `http://localhost:8080/web/hello` in your web browser, you should see “Hello, World!” displayed.
Conclusion
- `@Autowired`: Used for automatic dependency injection in Spring.
- Example: Demonstrated how to use `@Autowired` to inject a `GreetingService` into a `HelloController` class using constructor injection.
